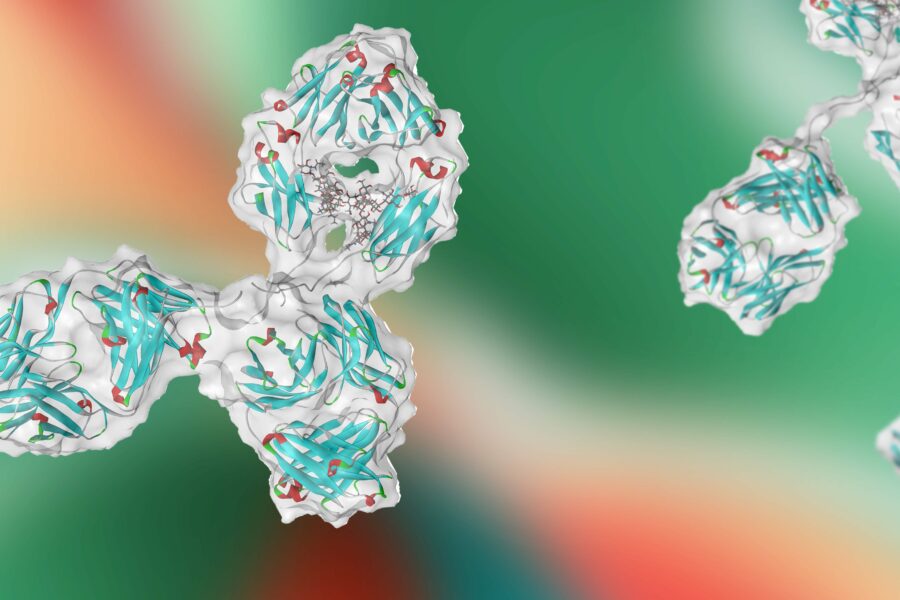
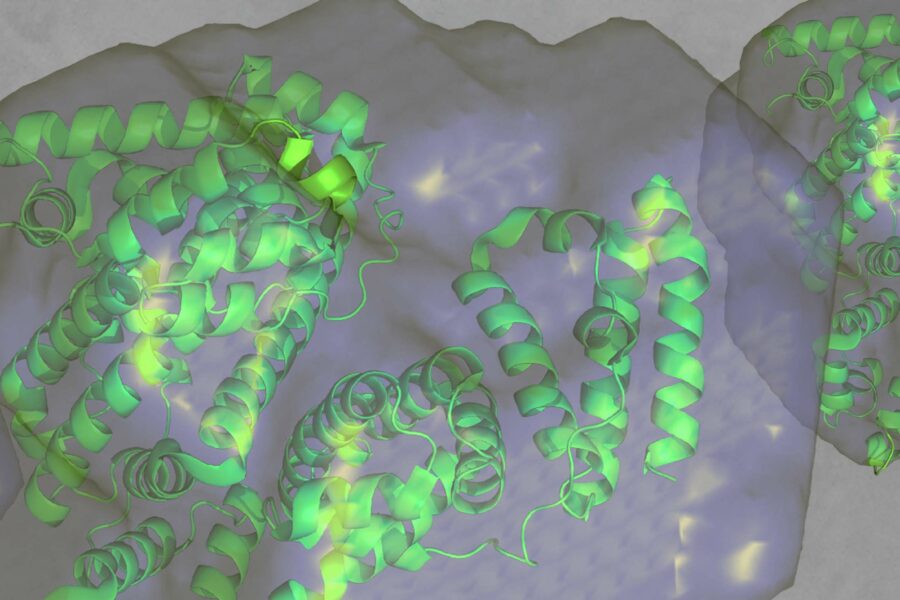
Probing Antibody conformation and interactions with SAXS: Effects of Concentration and Salt
Biotherapeutics, particularly monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), are well-established therapies recognized for their...
SAXS: an efficient tool for studying the size and structure of small peptides
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) is a versatile technique for analyzing small peptides in solution, offering detailed insights into their size, structure, and self-assembly.
Laboratory SEC-SAXS: a comprehensive approach to biological sample analysis
The structural and conformational stability of biological samples presents significant challenges due to...
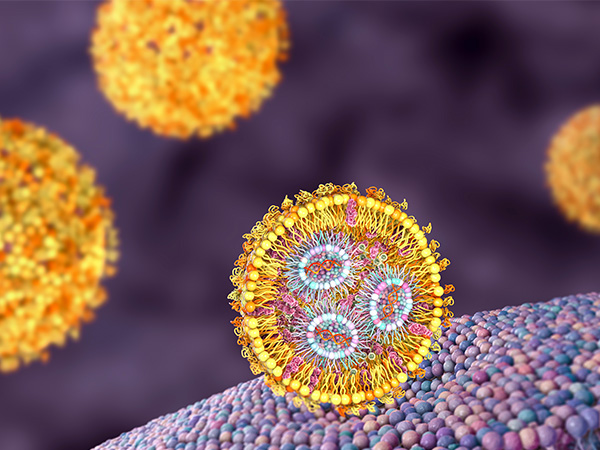
Phase diagram of lipid nanoparticles obtained with SAXS
Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) have attracted considerable attention as promising drug carriers due to their biocompatibility and ability to encapsulate...
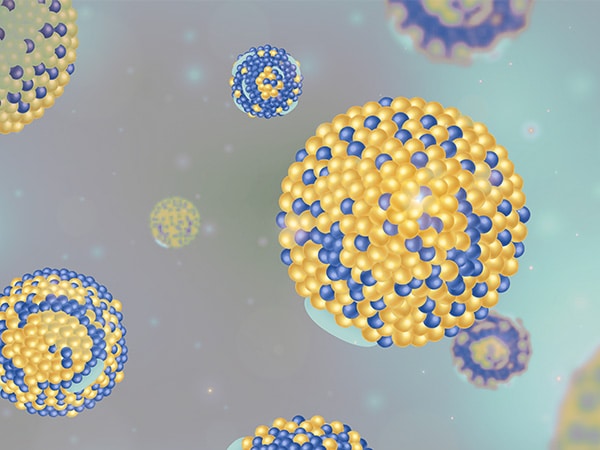
SAXS as a tool to study Lipid Nanoparticles
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are one of the most exciting technologies in the drug delivery world. Previously used to study lipid nanoparticles and lipoplexes, small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) has proven to be an excellent technique for characterizing the structure of LNPs.
Shear alignment of Pluronic block copolymers
The structural evolution of P123 Pluronics was monitored and analyzed through shearSAXS measurements performed with the Xenocs Couette stage Poloxamers, also known under commercial names as Pluronics®, Synperonics® or Kolliphor® are a class of synthetic triblock copolymers that are composed of polyethylene oxide (PEO) and polypropylene oxide (PPO) blocks. They…
Shearing of clay minerals in suspension
Investigation of smectite suspension shear behavior through SAXS measurements performed with the Xenocs Couette stage Clay minerals are a group of hydrous aluminosilicate minerals that are commonly found in soils, sediments, and rocks. The most common types include kaolinite, illite, and smectite, each with its own distinct characteristics and uses.…
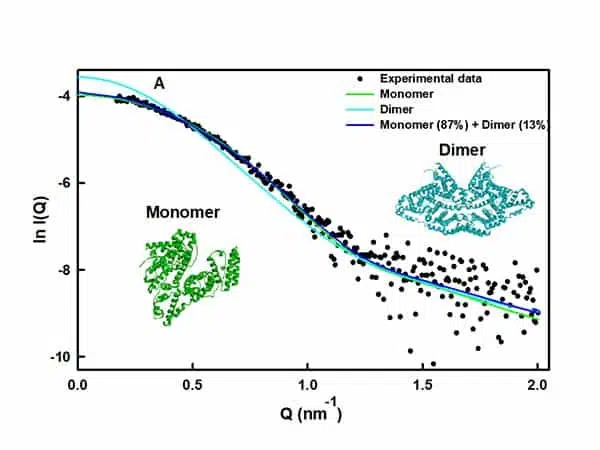
Characterization of protein intermolecular interactions
SAXS was used to study the effect of pH and protein concentration on the self-interaction process of a BSA system in solution Bovine serum albumin (BSA) is a non-glycosylated globular protein found in bovines. It is widely used in drug delivery, immunodiagnostic procedures and in clinical chemistry due to its…
Characterization of protein self-association
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) is a non-glycosylated globular protein found in bovines. It is widely used in drug delivery, immunodiagnostic procedures and in clinical chemistry due to its low cost and...
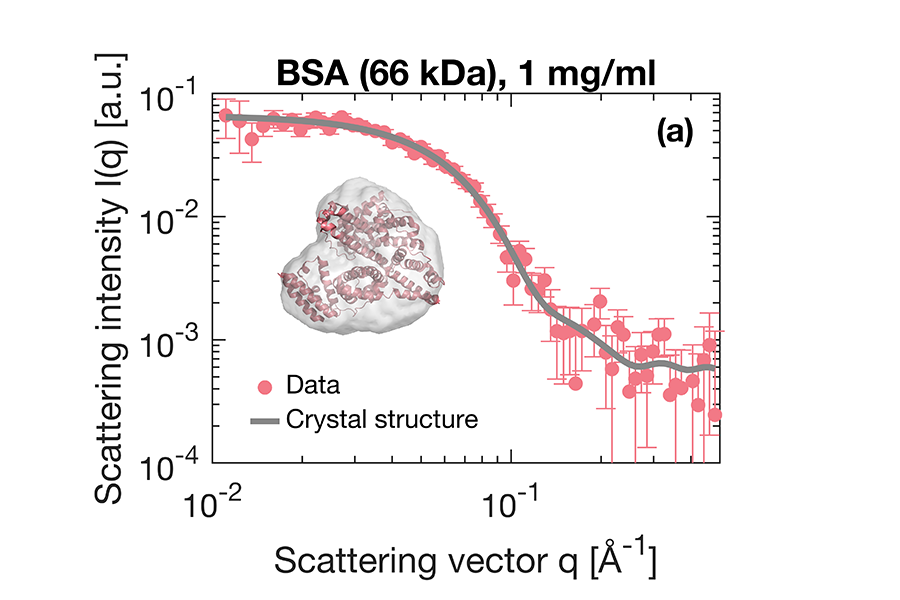
In-lab SEC-SAXS for structural investigation of complex samples
How to study the structure of complex biological samples? High quality data and 3D envelopes can be obtained on small and large proteins with SEC-SAXS in the lab Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) is commonly used to investigate the solution structure of biological macromolecules. Highly accurate results can be obtained with…